Difference between revisions of "Heatsink"
m |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Otherlang2 | {{Otherlang2 | ||
}}{{SB Infobox Begin | }}{{SB Infobox Begin | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
}} | }} | ||
}}<section begin=summary/>A heatsink is an integral part to most high-performance [[Generator (Assembly)|power plants]], and is used to rapidly store or transfer [[Heat mechanics|heat]] away from generators.<section end=summary/> | }}<section begin=summary/>A heatsink is an integral part to most high-performance [[Generator (Assembly)|power plants]], and is used to rapidly store or transfer [[Heat mechanics|heat]] away from generators. Heatsinks also double as [[ducts|Duct]].<section end=summary/> | ||
== Usage == | |||
Heatsinks facilitate the interaction between devices that produce heat (such as [[Generator unit|generators]], [[Fuel chamber|fuel chambers]], and [[Mounted weapons|mounted weapons]]) and the devices that can dissipate heat (such as [[Radiator|radiators]]). Heatsinks can be used to effectively bypass the transfer limitation for heat that exists between devices and radiators, as their thermal transfer limitation is significantly higher. Despite their significant visual differences, each heatsink style has the same effective mass and thermal properties. | |||
== Types == | == Types == | ||
| Line 23: | Line 25: | ||
|{{SB Infobox Header | |{{SB Infobox Header | ||
|image=[[Image:Heatsink cube.png]] | |image=[[Image:Heatsink cube.png]] | ||
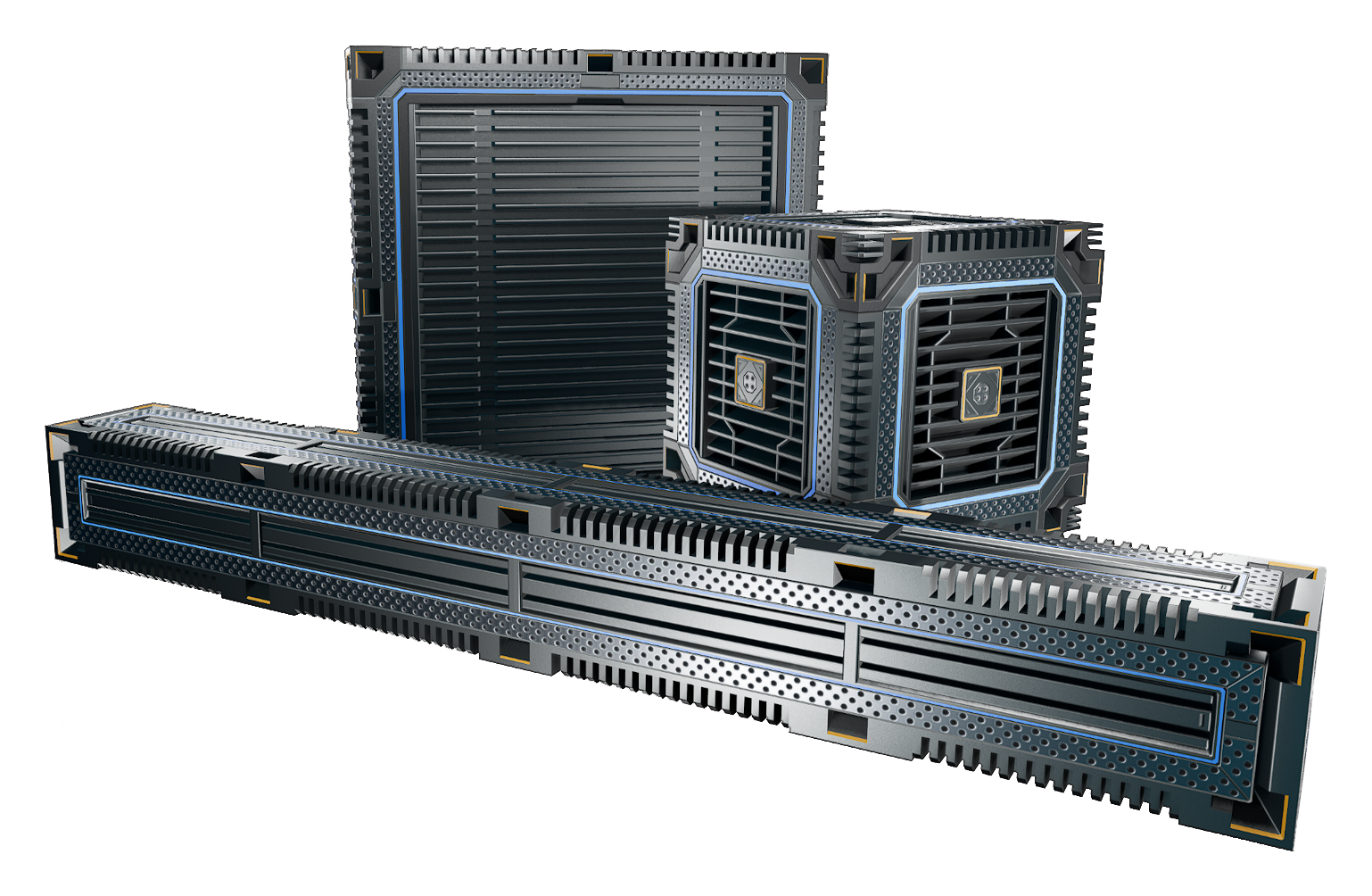
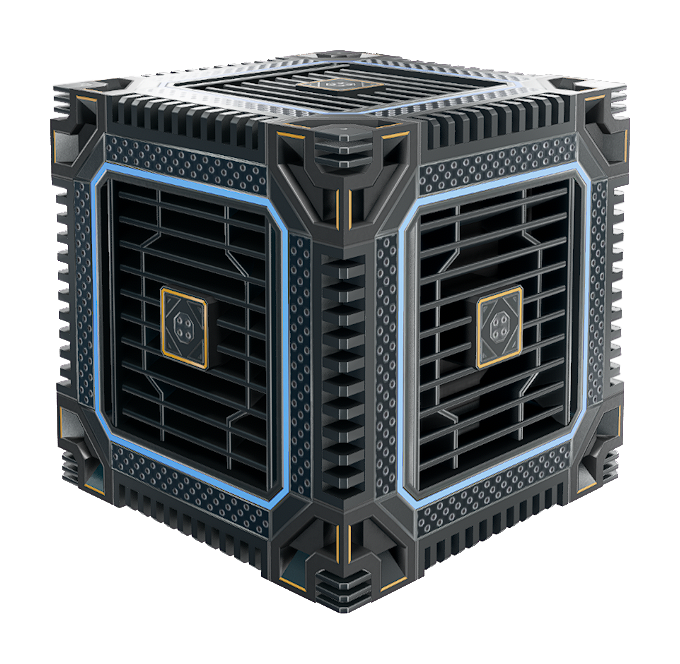
|name=Heatsink, | |name=Heatsink, Cube | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 35: | Line 37: | ||
|{{SB Infobox Device IO | |{{SB Infobox Device IO | ||
| | |heatDissipation=50 per second | ||
|heatCapacity=15,000 | |heatCapacity=15,000 | ||
|heatTransfer=750 per second | |heatTransfer=750 per second | ||
| Line 51: | Line 53: | ||
|{{SB Infobox Header | |{{SB Infobox Header | ||
|image=[[Image:Heatsink panel.png]] | |image=[[Image:Heatsink panel.png]] | ||
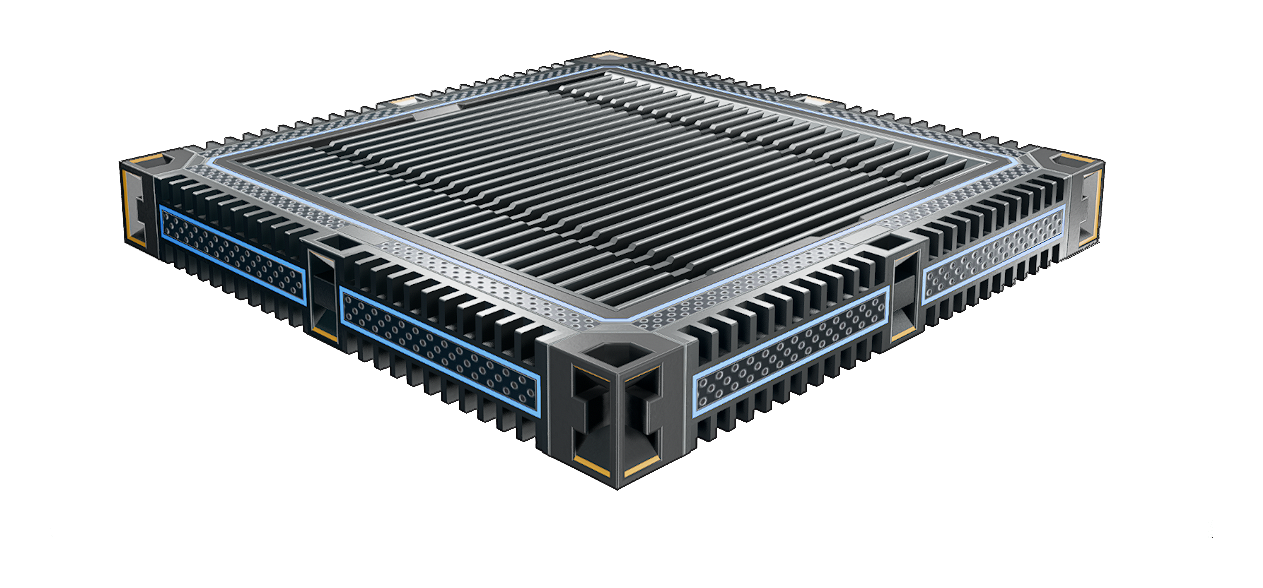
|name=Heatsink, | |name=Heatsink, Plate | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 63: | Line 65: | ||
|{{SB Infobox Device IO | |{{SB Infobox Device IO | ||
| | |heatDissipation=50 per second | ||
|heatCapacity=15,000 | |heatCapacity=15,000 | ||
|heatTransfer=750 per second | |heatTransfer=750 per second | ||
| Line 78: | Line 80: | ||
|{{SB Mini Infobox Begin | |{{SB Mini Infobox Begin | ||
|{{SB Infobox Header | |{{SB Infobox Header | ||
|image=[[Image:Heatsink | |image=[[Image:Heatsink rod.png]] | ||
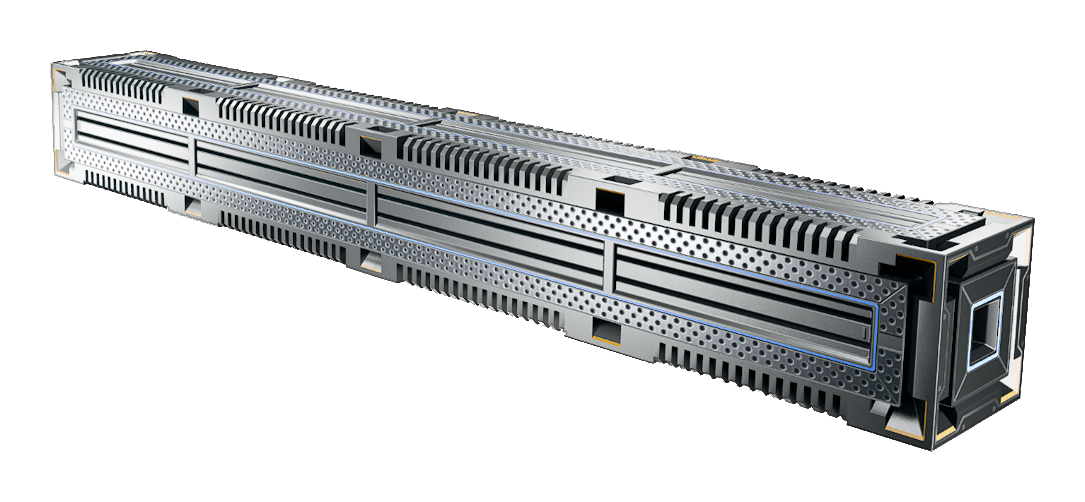
|name=Heatsink, | |name=Heatsink, Beam | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 91: | Line 93: | ||
|{{SB Infobox Device IO | |{{SB Infobox Device IO | ||
| | |heatDissipation=50 per second | ||
|heatCapacity=15,000 | |heatCapacity=15,000 | ||
|heatTransfer=750 per second | |heatTransfer=750 per second | ||
| Line 104: | Line 106: | ||
}} | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
== Device fields == | |||
<section begin=deviceFields/> | |||
===[[Heatsink|Heatsink]]=== | |||
{|class="wikitable" | |||
! YOLOL field | |||
! Description | |||
! Range | |||
|- | |||
! '''HeatTransferRateLimit''' | |||
| Maximum heat transfer to radiators, expressed as a percentage | |||
| 0 - 100 | |||
|- | |||
! '''HeatTransferRate''' | |||
| Current heat transfer to radiators, expressed as a percentage | |||
| 0 - 100 | |||
|- | |||
! '''HeatsinkStoredHeat''' | |||
| Amount of heat stored inside the heatsink | |||
| 0 - 15,000 | |||
|- | |||
! '''HeatsinkMaxStoredHeat''' | |||
| Maximum value for heat storage | |||
| 0 - 15,000 | |||
|- | |||
|}<section end=deviceFields/> | |||
To learn more about how to use fields, consult these wiki pages: | |||
* [[Universal tool|Universal Tool]] | |||
* [[Data networks|Data networks]] | |||
* [[YOLOL|YOLOL]] | |||
[[Category:Devices and machines]] | [[Category:Devices and machines]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:26, 20 October 2023
A heatsink is an integral part to most high-performance power plants, and is used to rapidly store or transfer heat away from generators. Heatsinks also double as Duct.
Usage
Heatsinks facilitate the interaction between devices that produce heat (such as generators, fuel chambers, and mounted weapons) and the devices that can dissipate heat (such as radiators). Heatsinks can be used to effectively bypass the transfer limitation for heat that exists between devices and radiators, as their thermal transfer limitation is significantly higher. Despite their significant visual differences, each heatsink style has the same effective mass and thermal properties.
Types
Device fields
Heatsink
| YOLOL field | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|
| HeatTransferRateLimit | Maximum heat transfer to radiators, expressed as a percentage | 0 - 100 |
| HeatTransferRate | Current heat transfer to radiators, expressed as a percentage | 0 - 100 |
| HeatsinkStoredHeat | Amount of heat stored inside the heatsink | 0 - 15,000 |
| HeatsinkMaxStoredHeat | Maximum value for heat storage | 0 - 15,000 |
To learn more about how to use fields, consult these wiki pages: