Difference between revisions of "Socket"
(→Advanced Uses: added more uses) |
(→Advanced Uses: Added link to progress bar memory .fbe) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
A socket has 2cm and 24cm snapping points while being able to pass right through other objects, this makes sockets very useful for snapping other objects into place. | A socket has 2cm and 24cm snapping points while being able to pass right through other objects, this makes sockets very useful for snapping other objects into place. | ||
<section begin=progressBarMemory/> | |||
=== Progress bar memory === | |||
=== | Many [[Modular_displays|progress bars]] can be stacked inside a socket allowing for large amounts of data field storage in a small space. [https://github.com/Thaccus/Starbase-Nav-Suite/blob/main/Extras/MemorySocket80.fbe An example .fbe can be found here].<section end=progressBarMemory/> | ||
=== Extending connections === | |||
Sockets can be stacked together and used to extend a connection point. | |||
=== Contactless | === Contactless connections === | ||
While [[duct]]s will transfer resources when touching, sockets will transfer resources to each other when close, without haveing to be directly attached. This can be used to create connections between rotating and sliding parts. Socket's ability to be placed inside other objects make them very useful for connections through the centre of a rotating part (eg. [[turntable]]s). | While [[duct]]s will transfer resources when touching, sockets will transfer resources to each other when close, without haveing to be directly attached. This can be used to create connections between rotating and sliding parts. Socket's ability to be placed inside other objects make them very useful for connections through the centre of a rotating part (eg. [[turntable]]s). | ||
Latest revision as of 22:02, 31 January 2023
The socket is a part generated by using the Socket tool.
Basic Usage
The most basic use of the socket is to mount display devices or buttons. By using the 'Seperate end placement' option single sockets can be placed, then moved around and bolted into place.
Advanced Uses
Sockets have a number of non-intended uses that can be very useful.
Cablepipes
The intended use of sockets was originally to pass pipe and cable connections through plates or other solid objects, since normal pipes and cables can also be placed straight through objects this use of sockets is not required. However the cables created by placing both ends of a socket are actually capable of transfering all resource types transferable by both cable and pipe! After creation, the sockets themselves can be removed if needed.
Scaffolding
Due to their ability to be removed without disturbing bolts or weld blocks, pass through all other parts and to be precisely placed sockets are ideal for use as scaffolding for extending bolts, or forcing them to lengths they otherwise would not reach, and for placing bolts/welds in places that would otherwise be impossible.
Snapping
A socket has 2cm and 24cm snapping points while being able to pass right through other objects, this makes sockets very useful for snapping other objects into place.
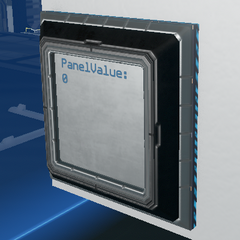
Progress bar memory
Many progress bars can be stacked inside a socket allowing for large amounts of data field storage in a small space. An example .fbe can be found here.
Extending connections
Sockets can be stacked together and used to extend a connection point.
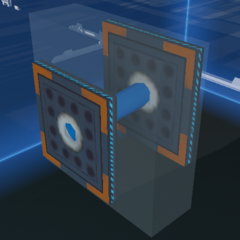
Contactless connections
While ducts will transfer resources when touching, sockets will transfer resources to each other when close, without haveing to be directly attached. This can be used to create connections between rotating and sliding parts. Socket's ability to be placed inside other objects make them very useful for connections through the centre of a rotating part (eg. turntables).