Difference between revisions of "User:DustyFB/Sandbox/Memory Relay"
| (16 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|ua=Реле пам'яті | |ua=Реле пам'яті | ||
}}{{User:DustyFB/Sandbox/Templates/Template:DeviceInfobox | }}{{User:DustyFB/Sandbox/Templates/Template:DeviceInfobox | ||
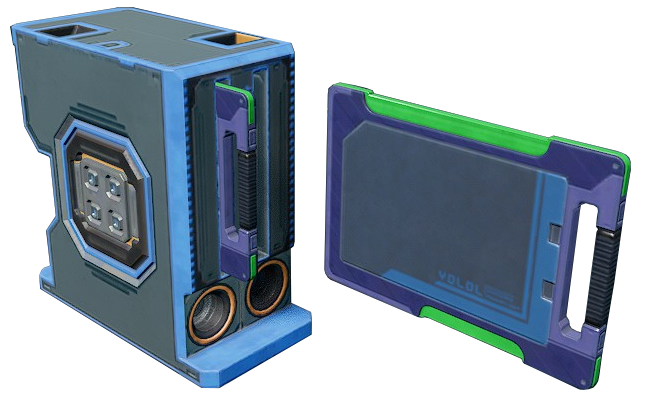
|image= | |image=[[Image:Memory_relay.png]] | ||
Image: | |||
|caption=A memory relay, and associated memory chip | |caption=A memory relay, and associated memory chip | ||
|name=Memory Relay | |name=Memory Relay | ||
|class1=hi | |||
|type1=hi | |||
<!-- Overview tab --> | <!-- Overview tab --> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 14: | ||
|availability=[[Luxury Items]] | |availability=[[Luxury Items]] | ||
|size=48 × 24 × 48 cm | |size=48 × 24 × 48 cm | ||
|weight= | |weight=409.84kg | ||
|volume=41.19kv | |volume=41.19kv | ||
|corrosionResistance=410 | |corrosionResistance=410 | ||
<!-- Usage section --> | <!-- Usage section --> | ||
| | |electricIn=Passive | ||
|sockets=4 | |sockets=4 | ||
| | |YOLOLchips=2 | ||
|modInterfaces=2 | |||
<!-- Resources section --> | <!-- Resources section --> | ||
|bastium=45% | |bastium=45% | ||
|corazium= | |corazium=10% | ||
|vokarium=25% | |vokarium=25% | ||
|ilmatrium=20% | |ilmatrium=20% | ||
}} | }} | ||
The memory relay is a device used to transfer | The memory relay is a device used to transfer data fields from one [[memory chip]] to another, allowing for [[Data networks#device_fields|device fields]] to be linked with different field names. | ||
Memory relays separate sub-networks allowing for one-way broadcasting of variable changes, enabling the creation of modular [[YOLOL|YOLOL]] systems. | Memory relays separate sub-networks allowing for one-way broadcasting of variable changes, enabling the creation of modular [[YOLOL|YOLOL]] systems. | ||
== Basic information == | == Basic information == | ||
Memory Relays are connected to two separate [[Data networks|data networks]] via cable sockets at both ends of the device, or via a connection to [[Modular_device_rack|modular device racks]]. Facing the device's 'front' (where the memory chips are inserted): | |||
* | * The left side of the relay acts as the "input" connection. | ||
* The right side of the relay acts as the "output" connection. | |||
When the relay is powered, changes made to device fields on the input chip will propagate to the corresponding device field on the output chip. Data which occupies a device field on the left side of the relay will be propagated to the device field with a matching index on the right side of the relay. For example: The data in device field #3 on the input (left) chip will be automatically propagated to device field #3 on the output (right) chip. However, both sides of the relay must be enabled for the data to propagate: Disabling either side will prevent this transfer. | |||
* Values between networks are not automatically synchronized. | |||
** This means that connected networks may contain different values for similarly named device fields. | |||
== Device fields == | == Device fields == | ||
The memory relay has two distinct sub-components which have unique device fields, as the left and right side of the device. These device fields can only be accessed by interacting with the appropriate sub-component. | |||
{|class="wikitable" | {|class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 64: | Line 63: | ||
* [[Data networks|Data networks]] | * [[Data networks|Data networks]] | ||
* [[YOLOL|YOLOL]] | * [[YOLOL|YOLOL]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:05, 21 May 2021
The memory relay is a device used to transfer data fields from one memory chip to another, allowing for device fields to be linked with different field names.
Memory relays separate sub-networks allowing for one-way broadcasting of variable changes, enabling the creation of modular YOLOL systems.
Basic information
Memory Relays are connected to two separate data networks via cable sockets at both ends of the device, or via a connection to modular device racks. Facing the device's 'front' (where the memory chips are inserted):
- The left side of the relay acts as the "input" connection.
- The right side of the relay acts as the "output" connection.
When the relay is powered, changes made to device fields on the input chip will propagate to the corresponding device field on the output chip. Data which occupies a device field on the left side of the relay will be propagated to the device field with a matching index on the right side of the relay. For example: The data in device field #3 on the input (left) chip will be automatically propagated to device field #3 on the output (right) chip. However, both sides of the relay must be enabled for the data to propagate: Disabling either side will prevent this transfer.
- Values between networks are not automatically synchronized.
- This means that connected networks may contain different values for similarly named device fields.
Device fields
The memory relay has two distinct sub-components which have unique device fields, as the left and right side of the device. These device fields can only be accessed by interacting with the appropriate sub-component.
| YOLOL field | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|
| IsMasterEnabled | On / Off, left side | 0 / 1 |
| IsEnabled | On / Off, right side | 0 / 1 |
To learn more about how to use fields, consult these wiki pages: